This publication discusses the principles and practices of grazing multiple species of livestock on pastures. Here, you’ll find a discourse on the benefits of multispecies grazing on productivity and profitability, including its positive impacts on pasture diversity and health. Also covered are grazing dynamics (how diverse animal species use grazing resources), the types and kinds of fencing and working facilities needed by various animals, and how to deal with predators, mineral supplementation and parasites. These considerations and topics can be useful when developing agrisolar operations that include livestock.
Tag Archive for: Agrivoltaics
This study was conducted to compare lamb growth and pasture production under solar panels and in open pastures in Corvallis, Oregon in spring 2019 and 2020. Results of the study dynamics of variations of shaded areas for rabbit habitat, seasonal herbage and forage production. These results can be useful in developing agrisolar operations that include rabbits.
This study was conducted to compare lamb growth and pasture production from solar pastures in agrivoltaic systems and traditional open pastures over 2 years in Oregon. The discussion dives into a variety of topics, including: reduction of pasture production due to trampling, production in fully shaded areas, herbage variation and its effect on lamb production and lamb behavior relating to water intake and shade usage. These considerations could be helpful for agrisolar development when lambs will be used for grazing, etc.
By: Wexus Technologies
Here’s a dirty secret: growers, processors, homeowners, and commercial businesses are spending too much money on solar energy installations. When many people think about their energy usage and getting relief from high electric bills, the first thing that comes to mind is to call a solar company for a quote. I’m here to tell you, pause and take a deep breath before making that call…
Don’t get me wrong, harnessing the power of the sun is an incredible technology. And the revolution of clean, renewable energy will help our future generations thrive for years to come. But the challenges with actually installing solar power reside in the upfront costs and return on investment.
If you call a solar company first, here’s what’s going to happen: they’ll take a look at your current energy bills and usage, and then size a photovoltaic (PV) system to match and offset your current energy usage. No doubt you will also want to size the system to match your usage, as the solar energy is cheaper than the energy you’d purchase from your local utility.
And keep in mind that solar is a 20 – to 30-year investment. So, if you purchase a solar PV system based on today’s usage, you could end up oversizing the system. And more importantly, you could overspend for unnecessary solar panels, particularly if your energy usage decreases, or energy prices change.
It’s the equivalent of flood irrigating a crop field for 24 hours straight, when drip irrigating for a few hours might do just as well, or better. So why do it the same way with energy?
What should you do instead?
Here’s a better approach to addressing your high electric bills: focus on the low-hanging fruit first. Smaller, lower-cost energy efficiency investments can have a larger impact on your energy usage and, ultimately, your bottom line. So, what are some examples of agriculture efficiency projects with high impact and high return on investment? Consider these:
- Selecting and continuously tracking your most cost-effective utility rate plan based on your actual energy usage
- Monitoring and maintaining irrigation pump efficiency above the industry –standard of 60%
- Irrigating during less expensive “off-peak hours” to avoid power demand surcharges
- Installing variable frequency drives (VFDs)
- Upgrading insulation and windows at cold-storage and food-processing buildings
- Installing LED lighting, lighting control systems, and daylight and motion sensors
- Upgrading to high-efficiency HVAC systems
The Wexus team calls this whole-farm, energy-saving approach “Reduce Before You Produce.” Before considering a solar PV installation, we highly recommend a “whole-farm” energy audit to determine a baseline of your historical usage, costs, and energy-consuming equipment across your entire farming operation.
For example, we’ve analyzed thousands of irrigation pumps. If one of your irrigation pumps is operating at 45% efficiency and the industry standard recommended level is 60%, you could be wasting tens of thousands of dollars every year. Simple preventive maintenance or repairs could cost a few hundred to a couple thousand dollars. However, they will be quickly paid back through energy savings in just a few months.
Now multiply these efficiency gains across all the irrigation pumps across your farm. Five pumps, 10 pumps, 20 pumps, 50 pumps, or more? The savings multiply as your operation grows. In this case, not only do you spend less money to generate kilowatt-hour (kWh) savings, but you also reduce the size and costs of any solar PV system, should you choose to install one.
After you’ve harvested your low-hanging “energy fruit” and driven the maximum energy savings possible across your farm, then it could be time to call the solar company to properly size a system for you.
Not convinced yet?
Here is a real-world example:
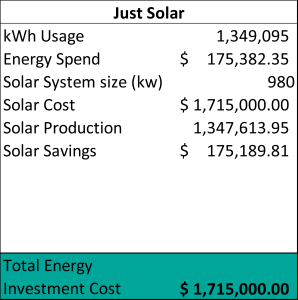
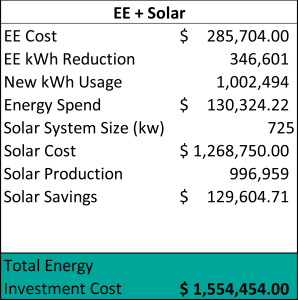
Above is a real-world example of one of our customer’s solar PV system investment costs before (and after) implementing energy efficiency projects. In this case, a farmer was leaving over $160,000 on the table by oversizing their solar PV system. What would you do with another $160,000 in operating income for your business?
The Montgomery Sheep Farm in North Carolina might be taking mixed use to another level. Not only is it a working sheep farm, it also offers a bed and breakfast for two-legged guests, breeds dogs, and is now using solar to power the entire operation. A WFAE reporter recently visited the farm and reports the farm’s 20-megawatt solar array has not only provided it with additional income related to clean energy, but keeps workers employed and has reduced costs.
One important solar benefit is a reduction in maintenance costs. The grass under the solar panels no longer needs to be cut, thanks to the sheep who graze under the solar panels on a rotating schedule. This not only reduces costs, but also allows the farm to raise more lambs per acre.
“We can have many more lambs per acre than if you put them on a normal pasture because of the solar panels,” Joel Olsen told WFAE, owner of the Montgomery Sheep Farm.
Olsen says another big benefit is the shade provided by the solar panels. The shade not only provides cool areas for the sheep during hot summer days, but it helps the grass grow thicker which means more food for the sheep. This thick grass is much more suitable for the sheep than grass typically grown in an open field, according to Olsen.
The farm currently operates on 200 acres, raising sheep, chickens, and horses. Roughly 400 sheep are rotated on a weekly basis under the solar panels in 30 designated grazing areas.
“If you can provide farmers additional income related to clean energy, additional income related to grounds maintenance, you know, it allows our rural areas to remain beautiful and have the people living there to remain employed,” Olsen said.
To learn more about the Montgomery Sheep Farm in North Carolina, listen to WFAE’s story, here.
AgriSolar Clearinghouse partner Greg Barron-Gafford, a professor at the University of Arizona, is looking to indigenous knowledge to find solutions to modern agricultural challenges through agrivoltaics. Barron-Gafford is part of a research team that is using an agrisolar approach to find solutions for agricultural challenges like water shortages and direct sunlight on crops in the desert.
Intense, direct sunlight in the desert and water shortages are both issues addressed by the researchers at the Biosphere 2 lab and the Tumamoc Resilience Gardens, in Arizona. Traditional techniques used by the American Indian tribes in the area for more than 5,000 years may offer solutions, and the measures are being tested in these facilities.
“Instead of relying on tree shade, we’re underneath an energy producer that’s not competing for water,” Barron-Gafford recently told the Washington Post.
Vegetation on site at the Biosphere 2 location will plant crops under solar panels as well as the traditional rock berms and rock piles used by area tribes.
“We’ve had 5,000 years of farmers trying out different strategies for dealing with heat, drought and water scarcity,” Gary Nabhan, an ethnobotanist and agrarian activist working at the Biosphere 2 location in Arizona, explained to the Washington Post.
Pairing solar with appropriate agricultural land may address the issues faced by desert farmers by shading crops from the intense Arizona sunlight, which can provide a cool area for plants to flourish under solar panels. Solar panels, unlike shade trees, don’t need water which means crops don’t have to compete for the scarce resource.
Not relying on irrigation canals to nourish thirsty crops such as leafy greens, nuts, and fruits means there is less of an impact on the immense amount of water that has typically been drawn from aquifers and, in Arizona’s case, the Colorado River.
Not only does an agrivoltaic approach to these challenges mean less impact on water supply, but it allows communities to build energy resilience.
Read more about the Biosphere 2 operation here, and the Tumamoc Resilience Gardens here.
Blueberries are big business in Maine, contributing upwards of $250 million to the state economy each year. That’s why a new partnership among blueberry growers, researchers, and the solar industry to harness the power of sun caught our attention.
“The potential for this project to pave the way in providing farmers with alternative income streams while still producing the iconic Maine wild blueberry is exciting, and we’re thrilled to be a part of it,” said Dr. Lily Calderwood, University of Maine Extension Wild Blueberry Specialist.
Currently, 38 U.S. blueberry farms contribute more than $4.7 billion to the economy annually. In Maine, blueberries contribute to $250 million to the economy.
“We’re pleased to be working alongside the University of Maine as well as industry leaders like Navisun and BlueWave Solar on this innovative project that will help promote the growth of the agrivoltaics market as well as support local farmers,” said Chris Ichter, director of business development at CS Energy.
Research indicates that the co-location of solar arrays with crops may reduce water usage by 30% and increase crop production by 70%. With an already large contribution to Maine’s economy, blueberry farmers, as well as others, may benefit greatly from combining crops and solar.
The pilot program outlined what are known as “dual-use challenges.” This study will attempt to understand some of those concerns by using half of the 10-acre project as a control group to study “optimal solar construction techniques.”
“CS Energy, Navisun and BlueWave Solar have all been incredibly engaged and cooperative throughout the whole process, which is crucial, as this is not only the first project of its kind for the University of Maine, but also for the entire state,” said Dr. Lily Calderwood, University of Maine Extension Wild Blueberry Specialist.
The research findings of this program will not only help future developers plan and execute effective dual-use systems, but ultimately will help support local farmers through advancing clean energy and discovering new income streams.
The Maces Pond Agrivoltaics Pilot Project in Rockport, Maine is the result of a collaboration between Bluewave Solar, Navisun LLC, and CS Energy, and the University of Maine. Read more about this partnership, here.
AgriSolar Clearinghouse partner Greg Barron-Gafford highlights the Biosphere 2 work in Agrivoltaics, including the application of biosphere techniques to fine-tune agrivoltaic crop growing.
The project includes citizen science that engages high-school students in a long-term agrivoltaic installation at the University of Rincon High School.
This video was produced by The Good Stuff.
AgriSolar Clearinghouse partner Greg Barron-Gafford describes the mutual benefits of growing crops under solar panels in large-scale solar arrays.
In this video produced by Arizona Public Media, Dr. Gafford explains these benefits through an ecological approach of a salsa garden understory and a solar panel overstory.
